Learnbillsoft's vision is to provide training & understanding of Billing application in BSS/OSS and Subscription Management Systems. The team is inclined to deliver quality functional and technical training.
Oracle BRM Blogs
Collapse All | Expand All
📊 Oracle BRM (OBRM) Data Model & Useful Queries .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following diagram is a high-level view of key tables and fields of BRM Database. For complete list of fields please refer BRM documentation: 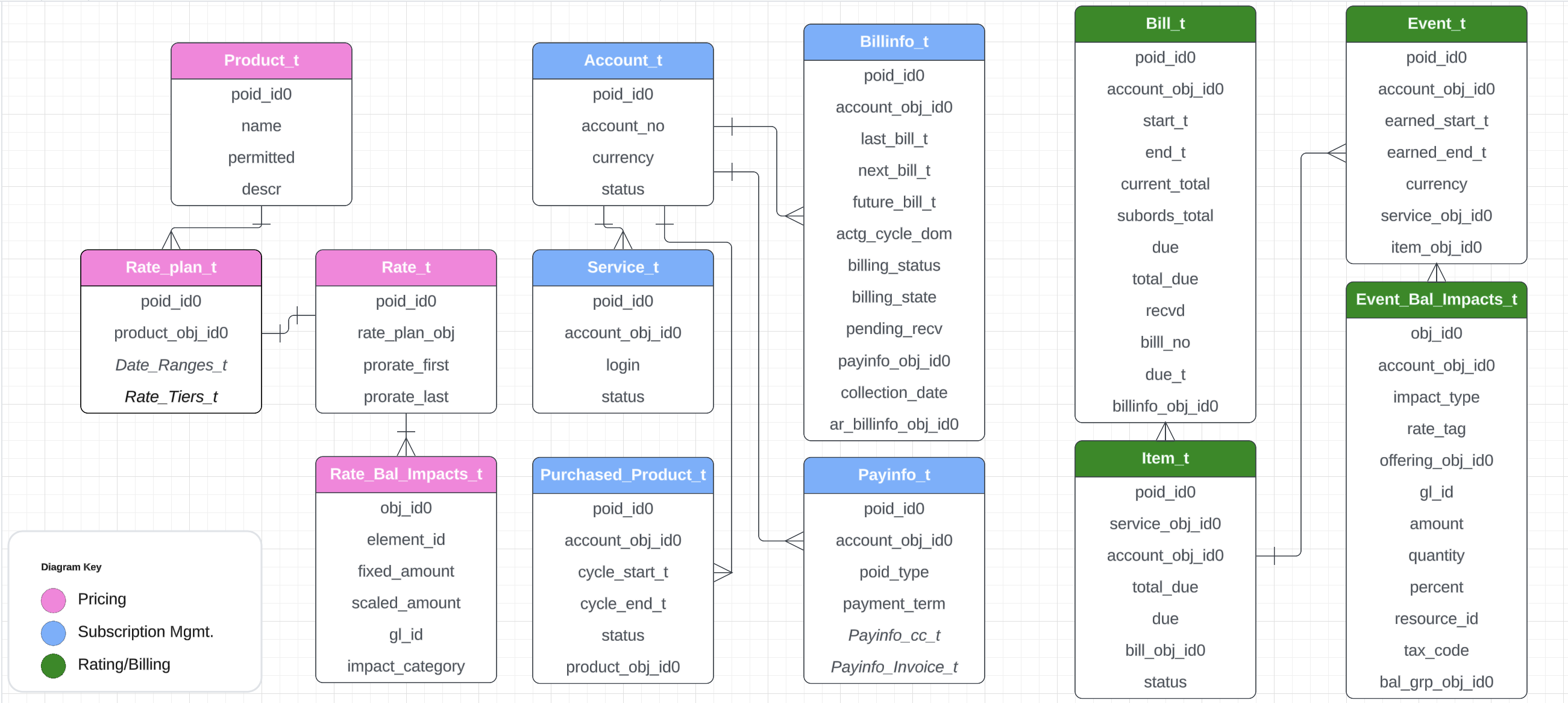 Queries for reference which are useful in all BRM projects: Sample Queries | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
⚙️ Oracle BRM Base Opcodes .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In Oracle BRM (Billing and Revenue Management), a base opcode is a fundamental operation or API used to perform actions such as creating, retrieving, updating, or deleting (CRUD) data in the system. These opcodes are predefined and serve as the building blocks for implementing business logic and processes within the BRM framework. Base opcodes examples:
Note: PCM_OP_BULK_WRITE_FLDS opcode is also used to update fields like PCM_OP_WRITE_FLDS opcode. This opcode is useful when we need to update the same set of fields across a large number of objects efficiently in a single operation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
⚡ Oracle BRM Standard/Policy/Custom Opcodes .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
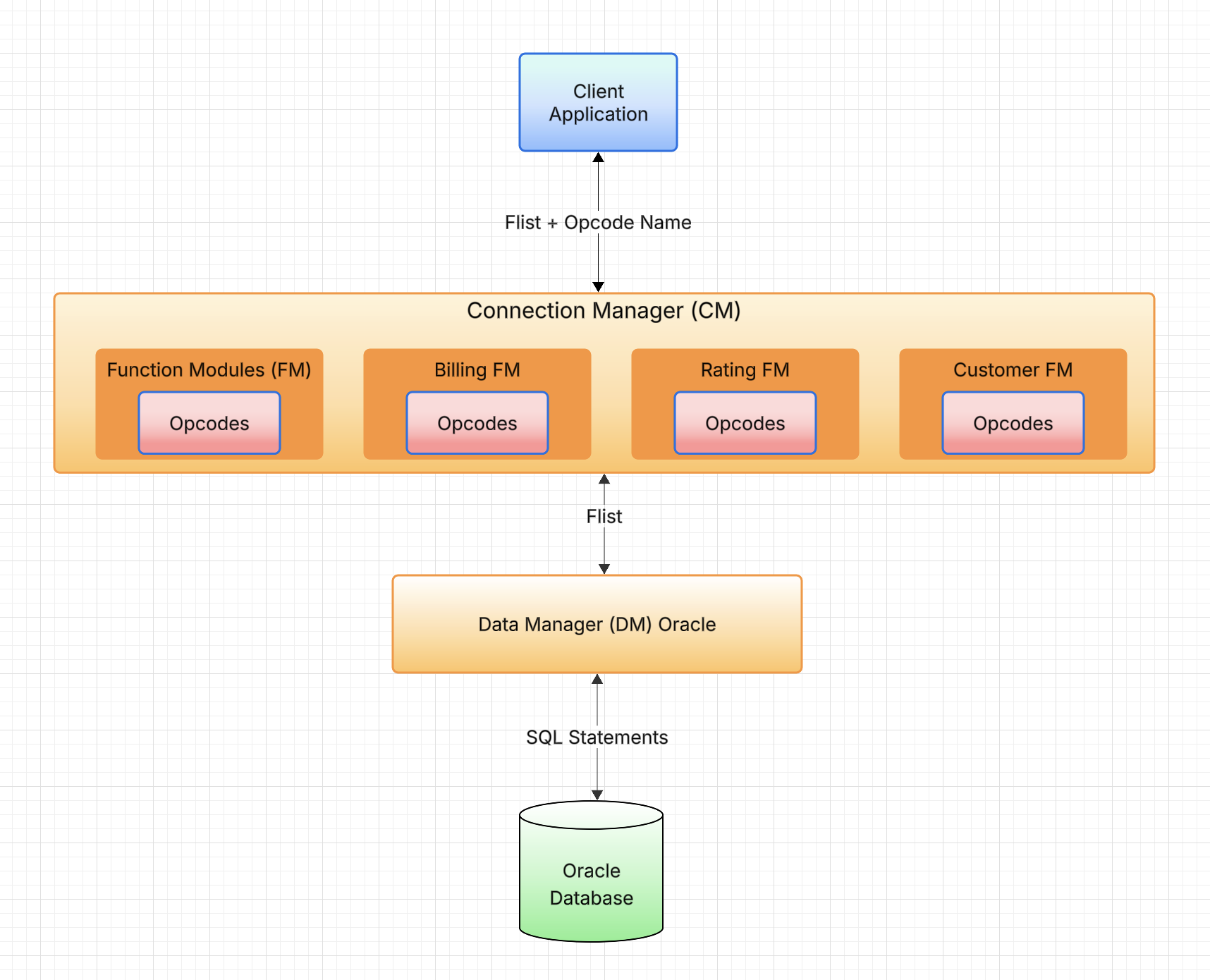
In Oracle BRM (Billing and Revenue Management), standard opcodes are predefined APIs used to handle tasks such as subscription management, balance adjustments, and service provisioning etc. They ensure consistency and reliability in processing business rules and transactions. Standard opcodes are BRM APIs which are part of BRM Function Modules (FM). Standard and Custom opcodes can be exposed as REST APIs to integrate with different applications. Below are some examples of Standard opcodes provided by Oracle Out-of-the-box from different modules:
Policy Opcodes are hooks provided in standard opcodes to implement customizations. They facilitate a wide range of functions, allowing for achieving custom requirements of billing and revenue processes. BRM provide a ".c" file for every policy opcode where developers can implement changes as per the business needs. Below are some examples of policy opcodes from different modules:
BRM also provides support for custom opcodes in order to fulfill business specific requirements in the project. Custom opcodes are designed with the input/output specifications and new library to meet such requirements. In order to invoke BRM API/opcode, Input payload needs to be prepared as per opcode specifications. Input Flists for Opcodes for Reference in all BRM Projects: View |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
🔧 Inbuilt OBRM functions and macros .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Below are some important functions/macros which are frequently used in BRM opcodes to implement different functionalities. Flist Management Macros-
Other Macros-
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
🔄 MTA with examples .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
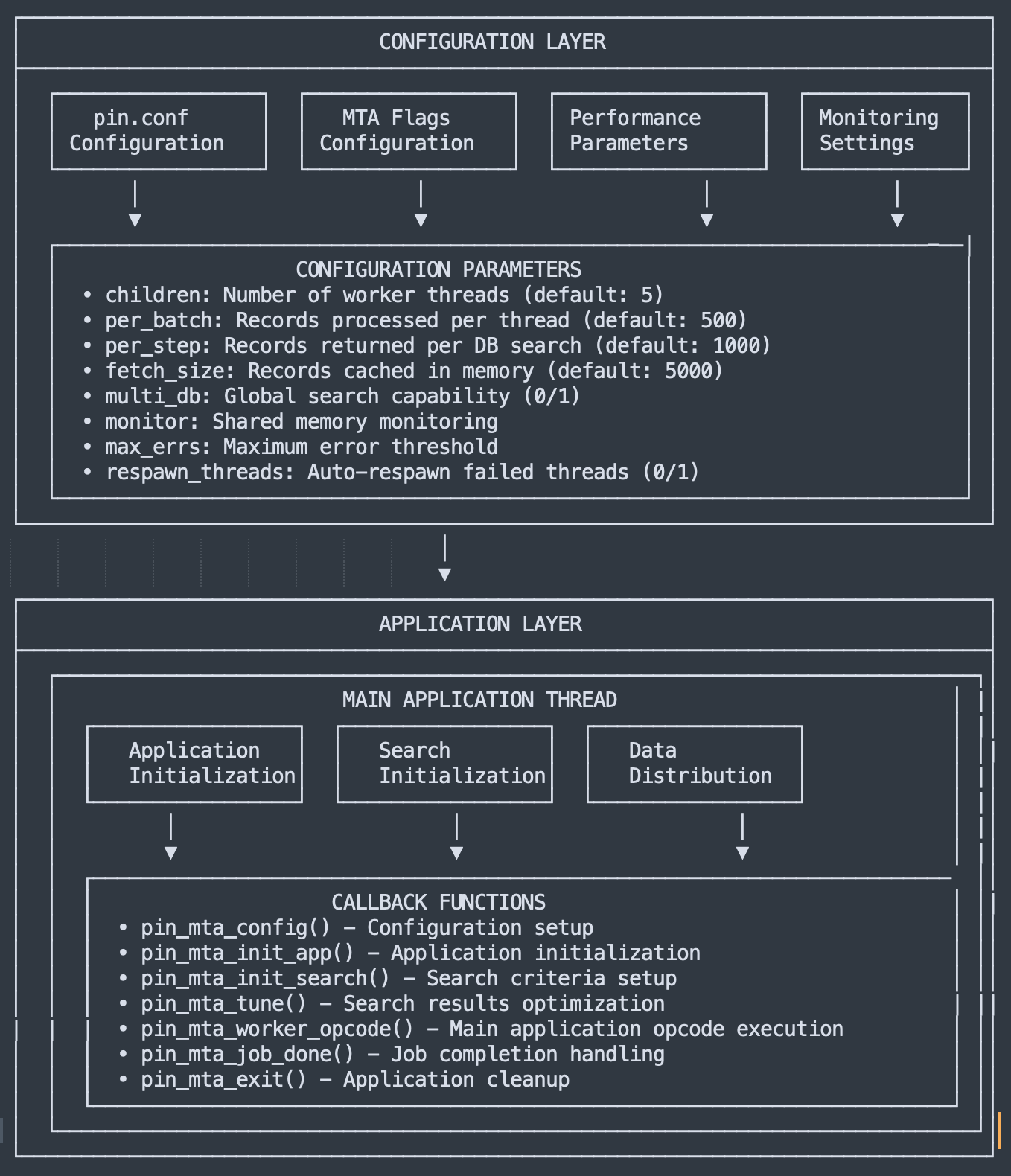
MTA application is implemented to process operations/opcode in batch mode. This multi-threaded application executes parallely for high volume processing. Also MTA can be implemented in order to execute API calls asynchrously. For example some requests can be recorded in staging table and can be processed in batch, which gives a better way of error handling and retry mechanism. 🔄 MTA Utility (Scheduled For Daily Run)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
🐛 Debug OBRM CNE deployments on Kubernetes .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deployment and monitoring of applications running as pods in Kubernetes(k8s) environment is done using helm & kubectl respectively.
Some useful helm commands:
Important kubectl commands:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
🏗️ Oracle ECE Architecture .. | Close | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
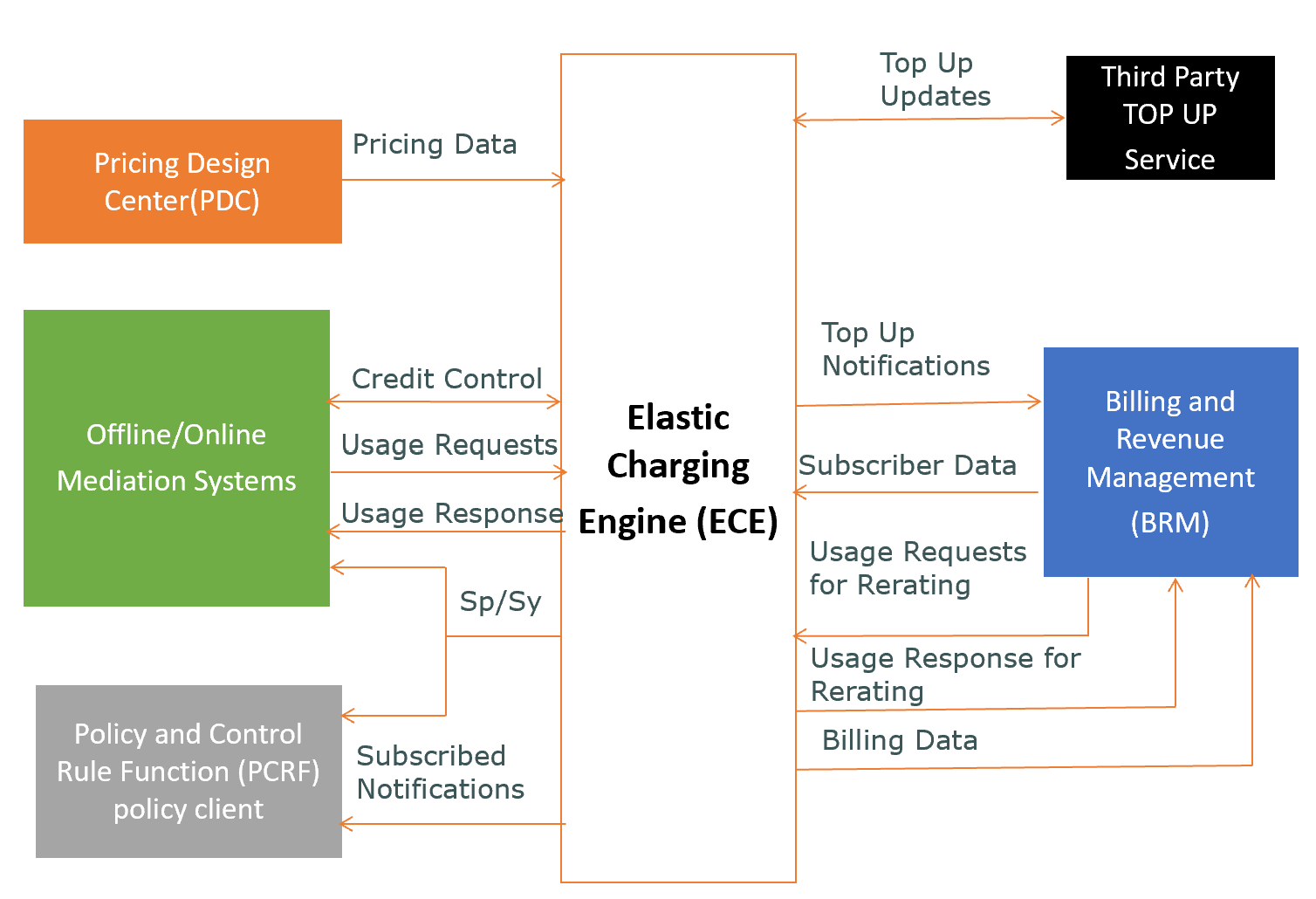
This shows ECE architecture and supported integrations with different systems like PDC, BRM, Mediation System etc.: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Please share the feedback of this blog on learnbillsoft@gmail.com to improve this blog.
Recordings: YouTube channel videos
HOME |
BRM BLOGS |
SUB BLOGS |
TECH BLOGS |
CONTACT US
© 2025 Learnbillsoft | Billing & Revenue Training Specialists