Learnbillsoft's vision is to provide training & understanding of Billing application in BSS/OSS and Subscription Management Systems. The team is inclined to deliver quality functional and technical training.
Subscription Monetization Blogs
Collapse All | Expand All
Quote-to-Cash Process .. | Close | |||||||||||||||
Quote-to-Cash also called as Quote-to-Revenue is an important process for Subscription Monetization. Below are the steps of the typical Quote to Cash process which supports Subscription Lifecycle of different businesses: 1. Product Configuration: According to the Business, products with the attributes are defined. 2. Pricing: In this step, sales and finance teams sets up the rate plan of the product. 3. Quoting: This is to generate accurate quotes for potential customers by CPQ system. 4. Contract Management: Once the quote is accepted, the contract is negotiated and created in CLM system. 5. Order Fulfilment: Order execution is initiated in CRM system. Order is synchronized to billing and fulfilment systems and delivered. 6. Billing:Invoice is generated and delivered to customers and payments are collected. 7. Revenue Recognition:In this step, Businesses recognise the revenue according to accounting standards. 8. Renewal: The final step is managing customer retention and subscription renewal for recurring revenue. |
||||||||||||||||
Subscription Management Usecases .. | Close | |||||||||||||||
The following diagram depicts some of the common Subscription Management Scenarios:
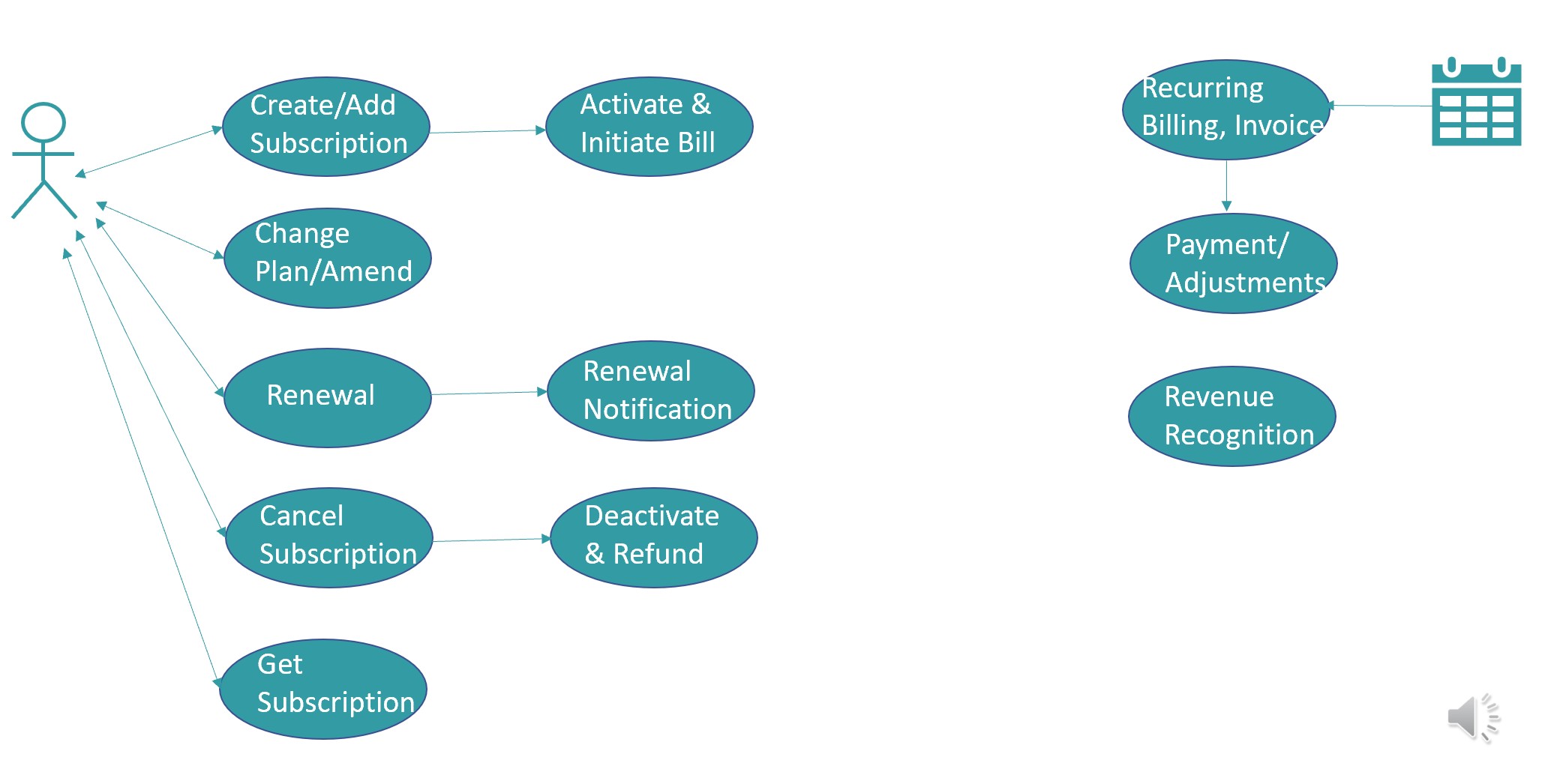 Below are few important features of different modules supported in Billing systems out-of-the-box or with customization:
| ||||||||||||||||
Billing System Modules .. | Close | |||||||||||||||
Below are the modules of any Billing application: 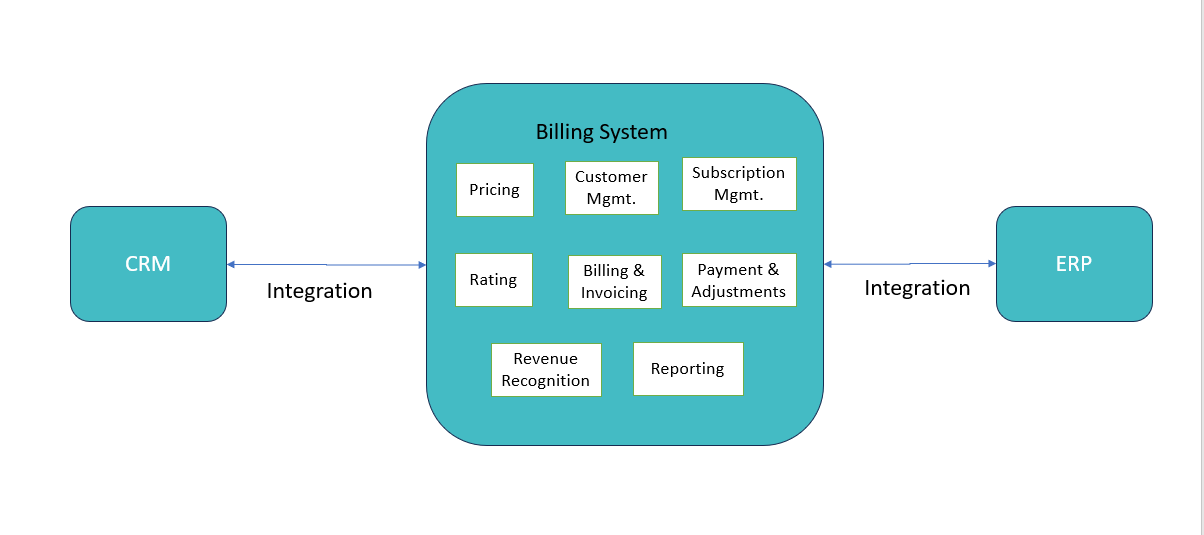 1. Pricing: Product catalog needs to configured as the first step for rating/billing any product/service. 2. Customer/Subscription Management: Accounts are created with the subscription offering purchased during order fulfilment. Subscription undergoes lifecycle changes like change plan, suspend-resume, cancel etc. 3. Rating: For services with usage charging, events are rated based on different event attributes like volume, duration etc. Recurring charges are also applied by this module based on product cadence/frequecy. 4. Billing & Invoicing: Customer is billed on the billing Day of Month. Invoice is generated and send based on customer preferred notification method. 5. Payment & Adjustments: After billing, payments are posted automatically if customer payment method is electronic. Otherwise customer initiats payment through different channels. 6. Collections/Dunning: For outstanding bills post due date, collection activities are initiated by system. System follows the Business rules configured for collections. 7. Accounting/Journaling: Revenue Recognition is done based on the Journal Run. Reports are generated based on different revenue types like Earned/Unearned revenue. 8. Integrations with upstream/downstream: Billing system integrates with CRM (upstream) for any subscription/account related changes. Also reports are send to ERP (downstream) systems from Billing. |
||||||||||||||||
Revenue Recognition .. | Close | |||||||||||||||
The following diagram highlights the 5-step model of Revenue Recognition in ASC 606:
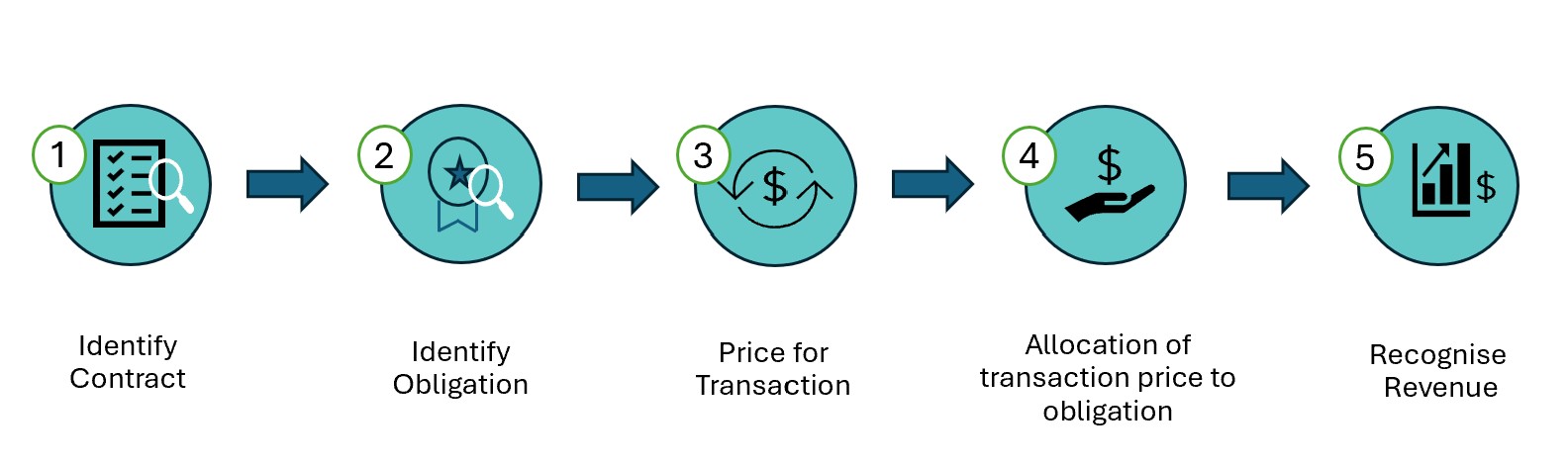 Revenue Recognition and reporting is one of the most important process which explains the Financial health of a company. This helps analysts and investors access the company's peformance over a certain period. In order to standardize processes around revenue recognition, a five-step framework for recognizing revenue is relevant under both GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards). The GAAP core principle for revenue recognition is that companies should recognize revenue when the revenue is "earned" i.e. goods or services are transferred to customers. This is implemented through a five-step process: 1. Identify the contract with a customer. 2. Identify the performance obligations in the contract. 3. Determine the transaction price. 4. Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations. 5. Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. Workflows for Revenue Recognition application: For Subscription business, Revenue Recognition (Rev Rec) and Allocation shall be based on the contract with the customer and ideally will be separate from Bill generation.
|
Please share the feedback of this blog on learnbillsoft@gmail.com to improve this blog.
Recordings: YouTube channel videos
HOME |
BRM BLOGS |
SUB BLOGS |
TECH BLOGS |
CONTACT US
© 2025 Learnbillsoft | Billing & Revenue Training Specialists
